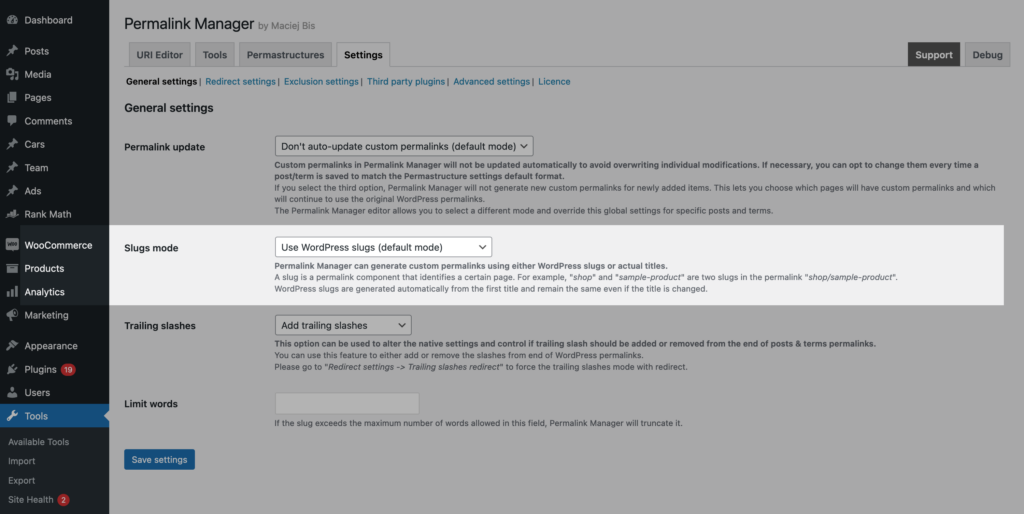
With Permalink Manager, you have the ability to customize how the default permalinks are generated for new posts and terms. In the plugin settings, you can select one of three available options in the "Slugs mode" field.
It is important to remember that the "Slugs mode" determines how the default permalinks are created for new posts or terms. This setting will not affect any existing content unless you use the "Regenerate/reset" tool. If you need to, you can manually overwrite any custom permalinks with the URI Editor and adjust them as necessary.
Available settings
Use WordPress slugs (default mode)
The native slugs are used by WordPress in posts' and terms' original permalinks. They are generated after the post or term is published. Please note that the slug remains unchanged even if you change the post/term title.
| Title | Native slug | Native permalink (slug is added to the end of URL) |
|---|---|---|
| Volvo XS60 | volvo-xs60 | http://example.com/car/volvo-xs60 |
| SUVs | suvs | http://example.com/cars/suvs |
Basically, the native slugs are used to identify the posts/terms when they are stored in the database. What is more important, they are also used in the native permalink system. WordPress parses the slug from requested URL and uses it to detect what post/term should be loaded.
In short, when you keep "Use native slugs" mode selected, Permalink Manager will use the same slugs as WordPress does for the default permalinks.
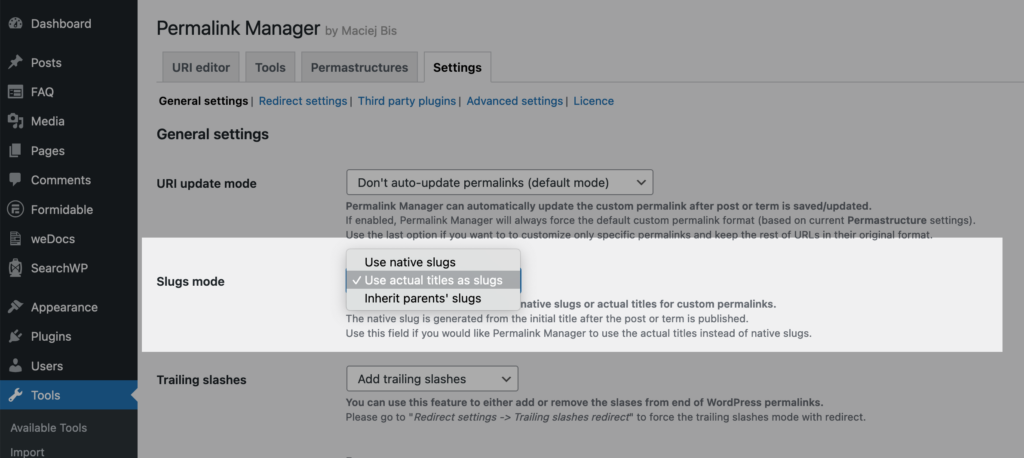
Use actual titles instead of WordPress slugs
Permalink Manager works differently than the native permalink system in WordPress. When a URL is requested and parsed by WordPress, the built-in permalink functions use the native slug to detect what content should be loaded. However, Permalink Manager uses the full URL address instead, providing more flexibility. It will recognize customized URLs as long as they are unique as a whole, regardless of whether they include native slugs or not. This is possible because the plugin stores statically in the database the full permalinks as a whole.
By default, Permalink Manager also uses native slugs when generating custom permalinks. However, if you would like to use actual titles rather than native slugs (which may be useful if you want to reuse the same slug for multiple pages), you can do so by selecting "Use actual titles instead of WordPress slugs" in the "Slugs mode" option box in Permalink Manager settings.
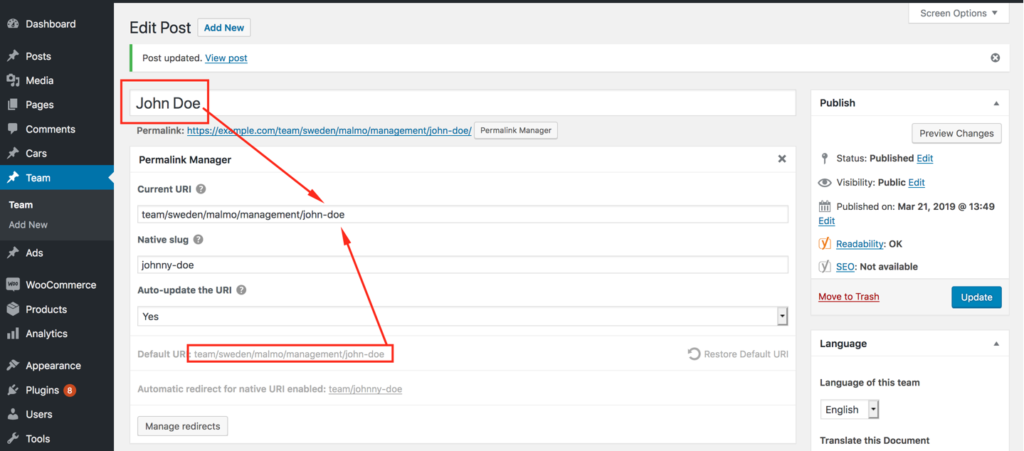
In the following example, you can see precisely how this works. By default, the permalink had the native slug 'johnny-doe' however in this mode it contains the actual title 'john-doe'.
Example
Another illustration of the difference between a native slug and a slug created from a title may be found in the table below. The the native slug is replaced with actual title not only for the specific page/term but also for its parents (see last column).
| Title & hierarchy | Native slug | Original permalink ("Use WordPress slugs") | Custom permalink ("Use actual titles instead of WordPress slugs") |
|---|---|---|---|
| Europe (Top-level) | european-countries | http://example.com/regions/european-countries | http://example.com/regions/europe |
| EU Europe -> European Union | european-union | http://example.com/regions/european-countries/european-union | http://example.com/regions/europe/eu |
| Scandinavia Europe -> European Union -> Scandinavia | scandinavia | http://example.com/regions/european-countries/european-union/scandinavia | http://example.com/regions/europe/eu/scandinavia |
This functionality could be also very helpful if you would like to use the same slug in more than one permalink. You can use the same slug more than once, but still you need to make sure that the full URL address is unique.
| Title | Native slug | Original permalink ("Use WordPress slugs") | Custom permalink ("Use actual titles instead of WordPress slugs") |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton T-shirt | cotton-t-shirt | http://example.com/shop/men/cotton-t-shirt | http://example.com/shop/men/cotton-t-shirt |
| Cotton T-shirt (Duplicated title) | cotton-t-shirt-2 | http://example.com/shop/women/cotton-t-shirt-2 | http://example.com/shop/women/cotton-t-shirt |
Inherit parents' slugs
This mode will be useful, if you would like make the child categories or pages inherit the permalink of their parent after it is manually adjusted.
| Title & hierarchy | Original permalink | Adjusted permalink | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apparel | http://example.com/shop/apparel | http://example.com/top-clothes | |
| Women | Apparel -> Women | http://example.com/shop/apparel/women | http://example.com/top-clothes/women |
| Jackets | Apparel -> Women -> Jackets | http://example.com/shop/apparel/women/jackets | http://example.com/top-clothes/women/jackets |
As you can see on above example, the custom permalink for top-category was changed from: shop/apparel to top-clothes. If inherit parents' slug mode is enabled, the default permalinks for child categories will be also affected.
Please note that after you change the parent permalink, the children permalinks will not be automatically updated. The new parent permalink will be inherited only by new terms and pages. For example, if you already have a structure of pages in a parent-child relationship and you change the parent's slug - you will still need to regenerate their permalinks. You can do so in Tools > Permalink Manager > Tools > Regenerate/Reset section.
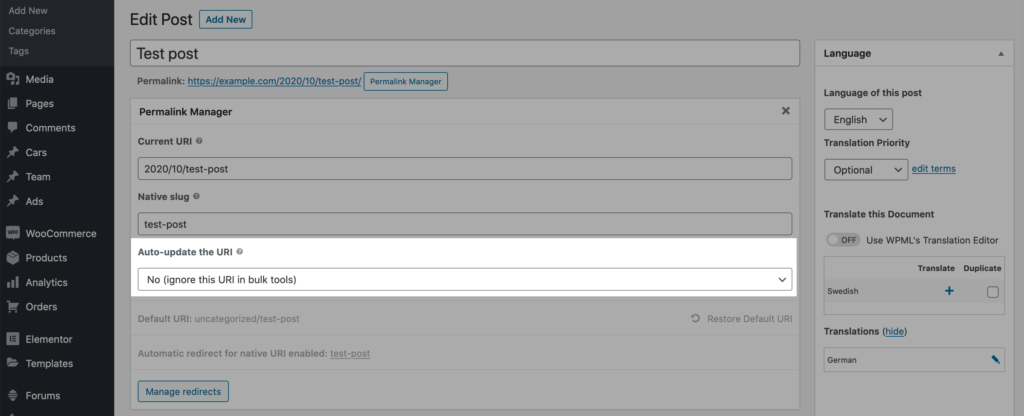
To prevent this from happening, you need to exclude parents permalinks to make Regenerate/Reset tool ignore them. As shown below, in URI Editor you should select "No (ignore this URI in bulk tools)" option in "Auto-update the URI" option field.
How to override the global settings
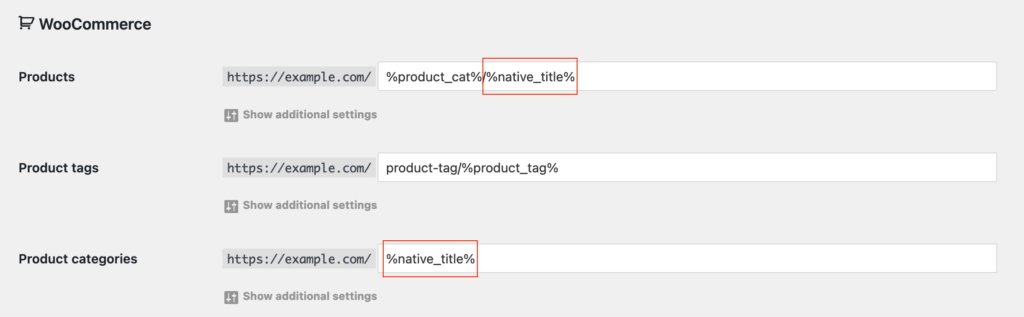
If you would like to use the actual title instead of native slugs only for selected content types, you can override the global settings by replacing default tags like %product% or %product_cat% with %native_title%.
Furthermore, you can also overwrite the global settings for selected post types or taxonomies programatically with additional code snippet.
How to use actual titles for selected taxonomies
Here is a sample snippet that shows how to configure Permalink Manager to use actual titles in the default permalinks of WooCommerce product categories, rather than slugs:
function pm_term_use_title_instead_of_slug( $mode, $slug, $object ) {
return ( ! empty( $object->taxonomy ) && $object->taxonomy == 'product_cat' ) ? 1 : $mode;
}
add_filter( 'permalink_manager_force_custom_slugs', 'pm_term_use_title_instead_of_slug', 9, 3 );How to use actual titles for selected post types
To complete the instructions, please find below a second code snippet showing how to override the global settings for post types (e.g., WooCommerce products) as well:
function pm_cpt_use_title_instead_of_slug( $mode, $slug, $object ) {
return ( ! empty( $object->post_type ) && $object->post_type == 'product' ) ? 1 : $mode;
}
add_filter( 'permalink_manager_force_custom_slugs', 'pm_cpt_use_title_instead_of_slug', 9, 3 );