The permalinks are simply URL addresses used by WordPress to distinct the content pages. The correct permalink structure is important for a number of reasons.
First of all, search engines will use your website URLs for search results. Secondly, they should attract the potential visitors to click on your links. The best permalink is one that allows readers to understand what the content is about.
By large, it is crucial to take into account the effect that the structure of your website's permalinks will have on the website hierarchy while developing the structure. A well-structured permalink structure may help search engines and visitors in understanding the relationships between pages on your website.
What Is the Definition of “Permalink”?
The term "permalink" pops up a lot in WordPress and other platforms. While it might sound like a complicated term, it is really quite simple. It is a combination of the words "permanent" and "link", which basically explains what it does.
It refers, technically speaking, to the whole URL address that is assigned to a specific post, page, or category. The word "permanent" suggests that even if the website changes, this particular link should, in principle, remain intact.
What Is the Difference Between URLs, Slugs and Permalinks?
URLs are part of your everyday internet use, even if you have never thought about them. Every time you visit a page online, the URL shows up in your browser. While many know what it is, some still confuse "URL" with "permalink". They are actually different things.
In general, all permalinks can also be considered URLs. This is so because permalinks are a subset of a URL, which is a more general term. While every permalink matches the definition of a URL, not every URL is automatically a permalink.

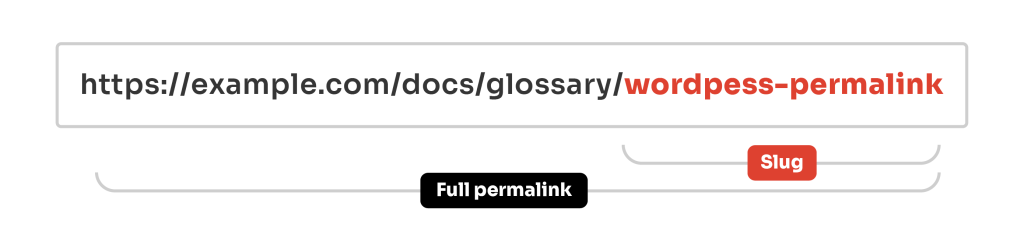
Slugs are another term you might hear when talking about URLs and permalinks. As you can see in the example below, a slug is just one part of the permalink. The slug is usually placed at the end of post, page, custom post type, and term (e.g. category) permalinks.
Permalink Plugins
A major issue many users face with WordPress is its limited ability to change permalinks. It only offers a few basic options for the URL structure.
When the default settings for customizing permalinks are insufficient, there are plugins that provide more flexibility. They allow users to fine-tune the permalink structure of their website to meet their individual requirements.
Unfortunately, there are not many reliable options, however the most popular plugins for changing WordPress permalinks are "Custom Permalinks", "Permalink Manager" and "Custom Post Type Permalinks".
How to Change WordPress Permalinks Without Plugin?
Now you should have no trouble differentiating between permalinks, slugs, and URLs. All of this was necessary so that you can understand what you may do with the basic WordPress settings.
Built-in Permalink Settings
The default permalink format in WordPress is not SEO-friendly since it includes numbers and query strings in the URL. For example, the default URL for a page may be like follows:
https://example.com/?page id=123
Since they are not particularly useful, permalinks structured in this way are not commonly used. The URL above provides no context or meaning for visitors or search engines. Needless to say, it is better to use something more readable instead of the initial setting.
You can find different permalink structures to choose from in the admin dashboard under "Settings > Permalinks".
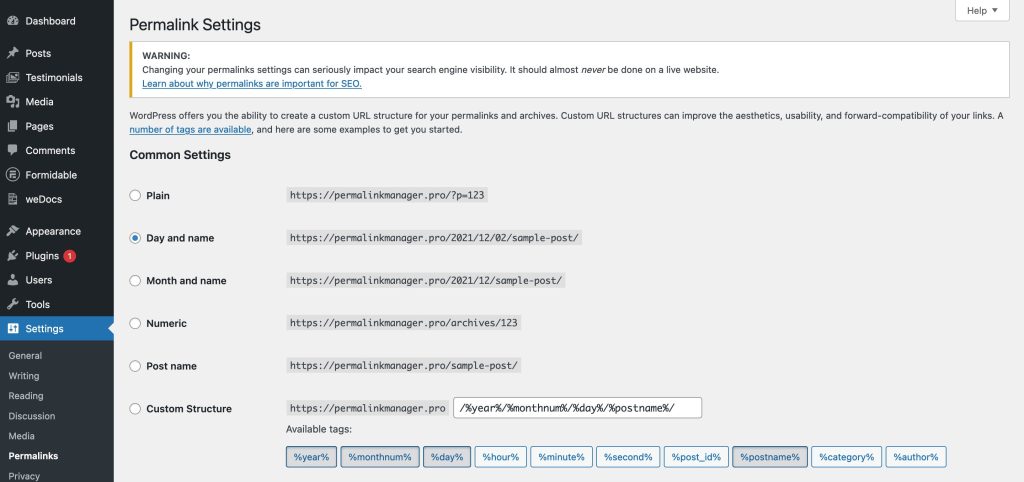
The following are the most common permalink structures. If you are interested, the WordPress documentation contains further information on this feature.
- Plain:
This structure use the standard URL syntax, which contains the post ID. That is not good for SEO or user experience. - Day and name:
This format includes the post's date and title in the URL. It is appropriate for news or magazine websites. - Month and post name:
This permalink structure includes the month and post name in the URL. It is appropriate for blogs or websites that publish content on a monthly basis. - Numeric:
This structure just contains the post ID. That is not good for SEO or user experience. - Post name:
This structure just contains the post name. It is the best structure for SEO and user experience.
How to Edit a Single URL?
If you want to change a permalink in WordPress, it is simpler than you may think. Depending on whether you are using the Block/Gutenberg editor or the Classic editor, the permalink section might be in a slightly different place, but the process is really the same.
via Classic Editor
The permalink field becomes visible as soon as you open the editing panel in Classic Editor. Under the title field, find the "Edit" button displayed next to the permalink. All you have to do is click it to change the permalink.
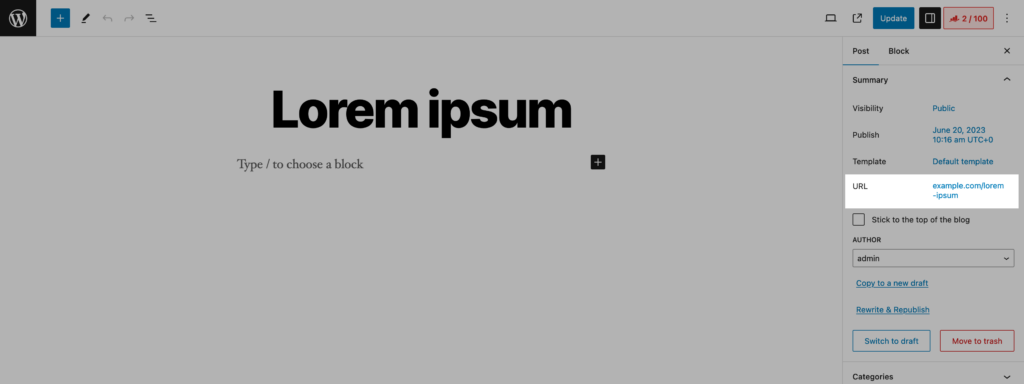
via Gutenberg Editor
The procedure is the same if you use the new Gutenberg editor. First, locate the "Summary" area on the right sidebar. When you find it, you will notice a "URL" field.
To open the popup, simply click the link displayed there. When you do this, a dedicated field appears where you may modify the slug, which is a section of the complete permalink.
Best Practices & SEO Tips
Listed below are some basic SEO tips and ideas to get you started. These suggestions include not just the official Google standards, but also the best SEO advice from industry insiders like Search Engine Journal.
Avoid Unnecessary Changes
Frequent changes to the URLs on a website can hurt search engine optimization. When URLs are changed often, it confuses search engines and wastes their "crawl budget" on pages that no longer exist.
Additionally, if a URL is changed after being crawled before, any backlinks or social shares for that page become broken. This negatively impacts SERP position and traffic from search engines. Stable URLs over the long run are better for maintaining visibility.
Furthermore, if you change a URL after it has been crawled, any current backlinks and social shares will become invalid, affecting your website's rating and traffic.
When creating a new page or post for publication, take the time to carefully select the appropriate URL and use it as the final permalink. Simply put, avoid changing your URLs in the future to avoid a drop in SEO score.
According to John Mueller, one of Google analysts, it is better to keep the old URLs intact as long as it is possible rather than to change them & redirect to new address.
301 Redirect Strategy for Keeping SEO Value
If you must change permalink for whatever reason, make sure to provide a 301 redirect as a fallback. This will signal the search engines that your content has been relocated to a new URL address.
Otherwise, some traffic may still be sent to pages that are no longer relevant. As a consequence, visitors will abandon your website if they discover the link is broken, resulting in a high bounce rate. In other words, your website's organic traffic might be slashed if a large number of visitors from search engines arrive at an error page or a blank page.
Keep Permalinks Simple
Keep your URLs short and simple. A permalink that clearly describes the page content will help with search engine optimization. In general, aim to keep the full URL under 100 characters. Theoretically, shorter, simpler URLs may rank higher in Google search results.
Custom post types like "portfolio" are often registered by WordPress plugins that create permalinks that contain hard-coded generic bases. Unfortunately, these do not appear to be understandable or beneficial from an SEO standpoint. Replace them with new bases (for example, "our-work" "products" and "team") that clearly reflect the structure of your website.
https://example.com/portfolio-cpt/foo-bar-com
https://example.com/our-work/foo-bar-com
Organizing your permalinks into a logical structure is a great way to improve their readability. This would facilitate crawling by search engines and user navigation.
However, keep in mind that while an ordered structure is good, keeping your permalink as short as possible should also be your priority. So, in your permalinks, avoid using any redundant folders or other long naming structures.
Permalink Manager allows the customization of post types' and taxonomies' permalinks. For instance, the plugin allows you to use the same URL structure for custom post type ("Band") items while also adding custom taxonomy slugs ("Genre") to their permalinks.
https://example.com/genres/80s/heavy-metal/ (Custom taxonomy: "Genre")
https://example.com/bands/ozzy-osbourne/ (Custom post type: "Band")
https://example.com/bands/80s/heavy-metal/ (Custom taxonomy: "Genre")
https://example.com/bands/80s/heavy-metal/ozzy-osbourne/ (Custom post type: "Band")
Avoid Overusing Keywords and “Stop Words”
There is no need to repeat the single keyword more than once. If your permalinks uses multi-level categories, you should also consider make their structure flatter.
https://www.example.com/animals-in-europe/birds-in-europe/big-birds/stark/
https://example.com/shop/apparel/women-shoes/high-leather-boots/
https://example.com/european-animals/birds/stark/
https://example.com/shop/women/apparel/footwear/leather/shoes/high-boots/
To make your permalink shorter, you can delete "stop words" like "the", "a", and "an". It is pointless to remove them from URLs that are already well-positioned. Nevertheless, for URLs for new content, it may still be a good idea considering your visitors.
https://example.com/blog/how-to-start-a-big-business-in-a-few-months
https://example.com/blog/start-business-in-few-months
Avoid Underscores and Special Characters
Underscores are uncommon in URLs, and for good reason. Google suggests using hyphens instead of them in one of their official guidelines. Hyphens are favored over underscores because they increase readability for viewers as well as search engines.
What exactly is the practical problem here? You should avoid the underscores, and remember to use the hyphens to separate the words.
https://example.com/kitchenappliances/digitalmicrowaveoven
https://example.com/kitchen_appliances/digital_microwave_oven
https://example.com/kitchen-appliances/digital-microwave-oven
Permalink Manager may be set up to include accented or non-Latin characters in custom permalinks if you wish to use them for whatever reason.
Although Google will be able to index your URL even if it contains spaces, commas, underscores & special characters. Remove them or replace them with dashes or Latin letters for improved reading.
https://example.com/countries,regions/balkan|southeastern-europe/Ελλάδα
https://example.com/countries-regions/balkan-southeastern-europe/ellada
Translate URLs to Reflect Content Language
Google is able to translate URLs on its own, so it can figure out what a page is about. However, URL translation may somewhat increase your user metrics and experience, both of which are ranking criteria.
Given that you are already localizing the content, why not translate the URLs as well? The disparity between content and URL language is not only inconvenient for users, but it also impacts SEO because keywords are dependent on the language of translated page. One of the videos on Youtube's official Google Search Central channel discusses multilingual URLs.
To sum it up, if your website is multilingual, you should translate the permalink bases. This might be extremely beneficial if your target market consists of customers from all around the world. Making your WooCommerce URL addresses have a distinct structure for each language will also aid your clients in navigating around your store.
https://example.com/en/books/history/herodotus
https://example.com/pl/books/science-fiction/stanislaw-lew
https://example.com/de/books/philosophy/friedrich-nietzsche
https://example.com/en/books/history/herodotus
https://example.com/pl/ksiazki/fantastyka/stanislaw-lew
https://example.com/de/bucher/philosophie/friedrich-nietzsche
Do Not Use .html at the End of URLs
Despite what some may think, adding file extensions to URLs makes no difference for search rankings. While the idea has persisted for years with some, Google has never treated extensions as a meaningful signal.
Google Search Central published detailed video that debunks this SEO myth, in case you still need more convincing.
The only exception is if you previously used a CMS that adds file extensions to the end of URLs, such as Magento. In such case, you can keep them after switching to WordPress. That way, any existing traffic to those URLs will not be lost.
https://example.com/music/hard-rock.html
https://example.com/music/hard-rock
Permalink Manager can help you if you switched from a different CMS to WordPress and wish to add .html to your new URLs to reconstruct the previous permalink structure.[/info]
Frequently Asked Questions
Is It Safe to Change Permalinks?
It is generally safe to change the URL of pages that have not yet been published. There is not a lot of wasted SEO potential here. These links have not yet been indexed or given backlinks by other websites.
However, modifying already indexed URLs may have an influence on your website's SEO rankings:
- Changing URLs can lead to broken links and the loss of valuable backlinks causing a poor user experience and negatively impacting search engine rankings.
- If 301 redirects are not implemented, search engines may penalize and devalue the new URLs because they see them as having duplicate content.
Google, for example, recommends arranging content such that URLs are formed logically and in a way that viewers can understand. This is only one of a few Google tips, so if you are interested, we recommend looking at others. As Google Search Central indicated in the video, altering URLs may make it difficult for search engines to crawl and index your website.
If the potential advantages of changing existing URLs are greater than the associated hazards, it is advisable to proceed with the modifications. For example, if you are changing URLs to improve user experience, rearrange your website, the possible risk to your website's SEO may be acceptable.
How Can Changing URLs Lead To Broken Links and Lost Backlinks?
Changing your website’s permalink structure can have unintended consequences. Any backlinks pointing to your pages may stop working if you do not set up redirects, leading to lost traffic and SEO value.
This can hurt your SEO because backlinks play a big role in search rankings. It can also reduce engagement from social media, as people who click on old shared links will not reach your content.
While updating URLs can make your site cleaner and more user-friendly, it is important to weigh the risks. Losing valuable backlinks and social shares can impact your site's performance.
Before making adjustments, be sure you have a solid plan to avoid setbacks. Weigh all the factors carefully and figure out what works best for your site.
How Long Does It Typically Take for Google to Index URL Changes?
It's difficult to determine the exact timeframe for Google to remove old permalinks and index new URLs. In general, Google may take a few weeks to a few months to fully crawl and index your website. Your website's page changes can take effect at different speeds depending on various factors. The size of your website, the number of modified pages, and the frequency of Google crawling your site are all factors to consider.
You may speed up the process by requesting a re-crawl of your website using Google Search Console. This will cause Google to reindex your website's pages and update its search results faster.