Permalink Manager is designed to work out-of-the-box with WPML and Polylang. You can use it to easily translate the permalink formats or define custom permastructure settings per language.
Managing multilingual URLs in WordPress often leads to conflicts, duplicated slugs, or limited control over translated permalinks. Permalink Manager gives you full control over URL structures across languages, without relying on rewrite rules or manual coding.
Setting Up Multilingual URL Structures with Permalink Manager
By default, WordPress uses the same permalink format across all languages. Multilingual plugins do not change this behavior automatically.
In WPML, this can be done by turning on the "Translate the slugs" option. This setting applies to the global base (e.g. "/store/") used by custom post types and taxonomies.
http://example.com/store/t-shirt/ (English)
http://example.com/es/store/camiseta/ (Spanish)
http://example.com/pl/store/koszulka/ (Polish)
Each content item still has its individual slug ("t-shirt", "camiseta", "koszulka"), which can be translated while editing the post, page, or term.
For users who need more flexibility, Permalink Manager offers a dedicated interface for this task. It supports both WPML and Polylang and allows full control over custom permalinks.
Step 1: Open Permastructure Settings
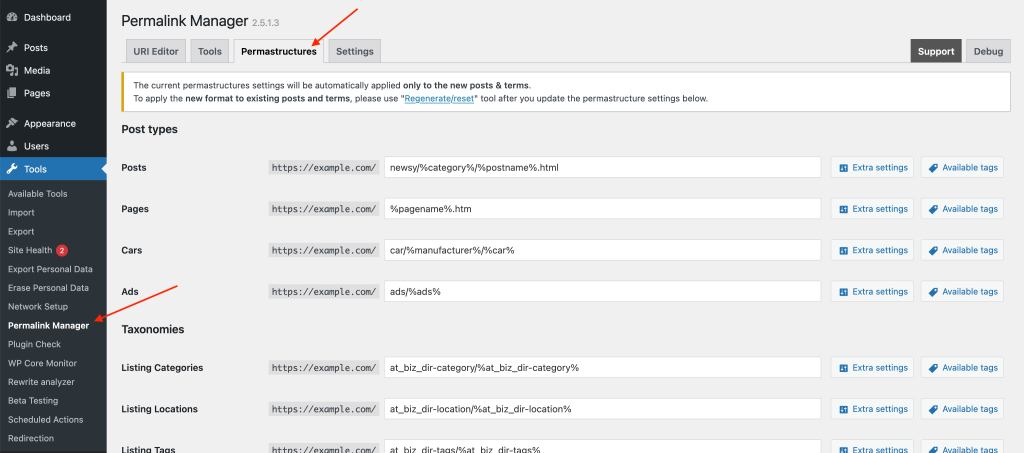
You can find the global settings for your URLs under "Tools -> Permalink Manager -> Permastructures". This section allows you to define custom formats, which we refer to as "Permastructures".
Opening the Permastructures editor displays input fields for all post types and taxonomies. At first, you will see just the field for the default language. This field also acts as a fallback for other languages if you have not customized their permalink formats.
Step 2: Define Per-Language Permalink Structures
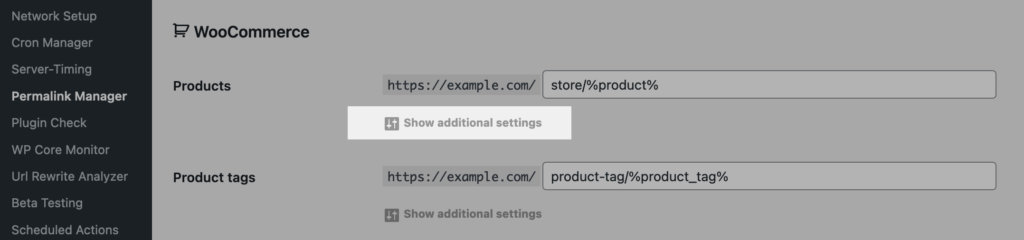
The plugin recognizes all the languages you have set up and lets you define a unique permalink structure for each one. To customize their URLs, click the "Show additional settings" button under the post type or taxonomy you want to edit.
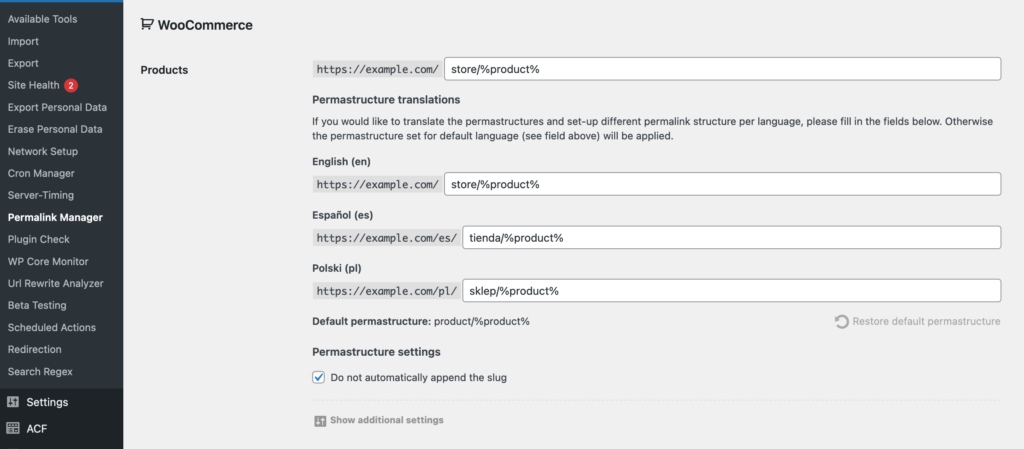
Once you click it, you will see separate fields where you can set the permalink format for each language added via WPML or Polylang. You do not have to fill in every language, so you can skip languages you do not want to change.
If a field is left empty, Permalink Manager will automatically use the default format from your website’s default language.
Step 3: Apply Changes and Translate Permalinks for Existing Content
By default, any changes you make to your permalink structure only affect new content. Existing posts, pages, and terms keep their URLs intact to prevent SEO issues.
Editing Translated Permalinks Manually
WPML
If you do not want to use the automatically generated custom permalink, you can change it for each post or page individually directly in the translation editor. Both the Classic and Advanced Translation Editor include separate fields for editing translated permalinks.
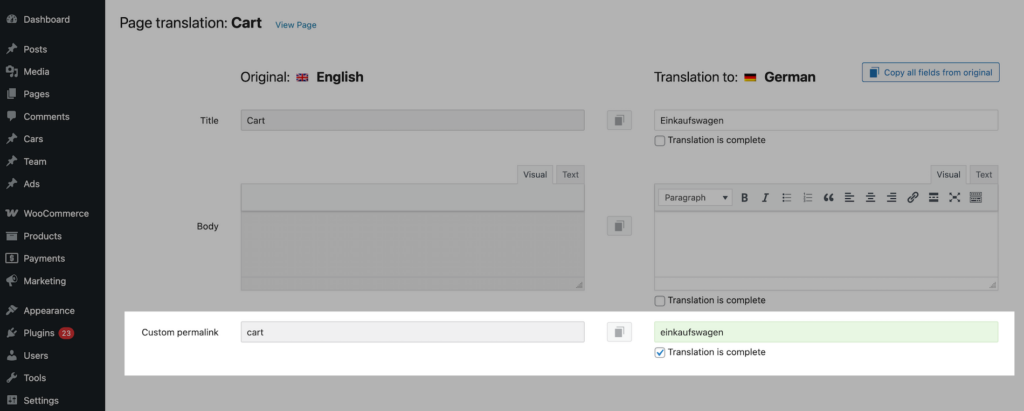
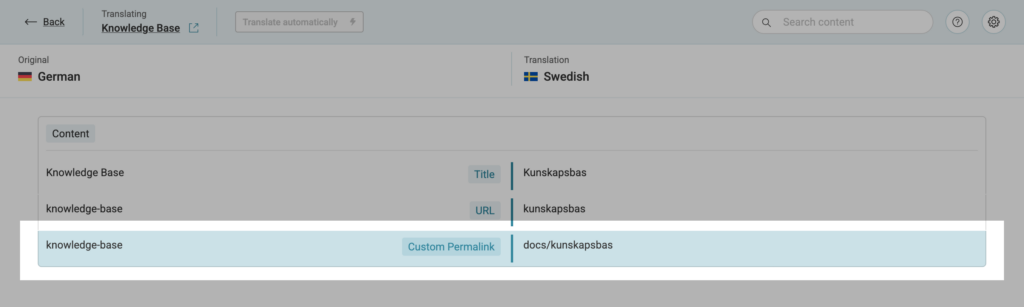
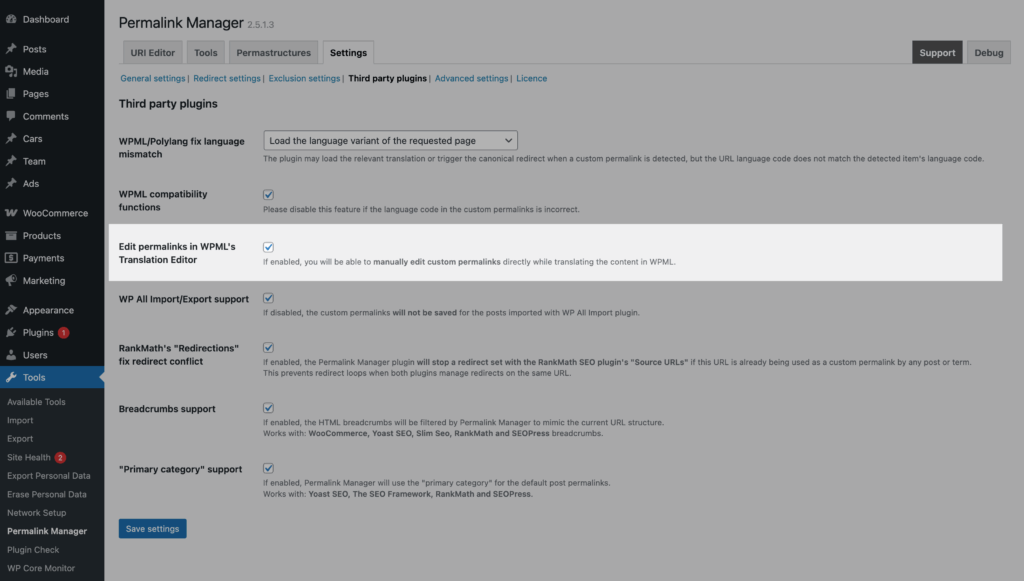
To enable this feature, enable "Edit permalinks in WPML's Translation Editor" option in the plugin settings before translating content. You can find it under the "Third Party Plugins" section in the plugin settings.
Polylang
The custom permalink editor works with Polylang translations out of the box without additional configuration. You edit the URL in the same screen where you edit the content.
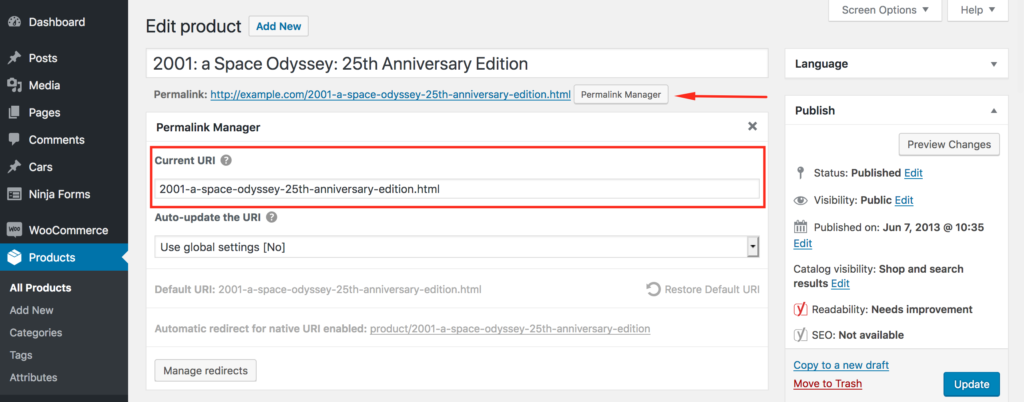
Each language version of a post, page, or taxonomy term has its own permalink. You can change these one by one using the same URI Editor described in the guide on changing permalinks.
FAQ & Troubleshooting
Does Permalink Manager Work with TranslatePress?
Unlike WPML and Polylang, which create separate posts for each translation, TranslatePress keeps translations in its own database tables, without creating separate post IDs.
You can use Permalink Manager to change URLs for posts and terms in the original language without any problem. Since translated items do not have unique IDs, it is not possible to edit their permalinks separately in Permalink Manager.
To translate their URLs, we recommend using the built-in TranslatePress translation editor. This allows the slugs to be translated automatically within your custom permalinks.
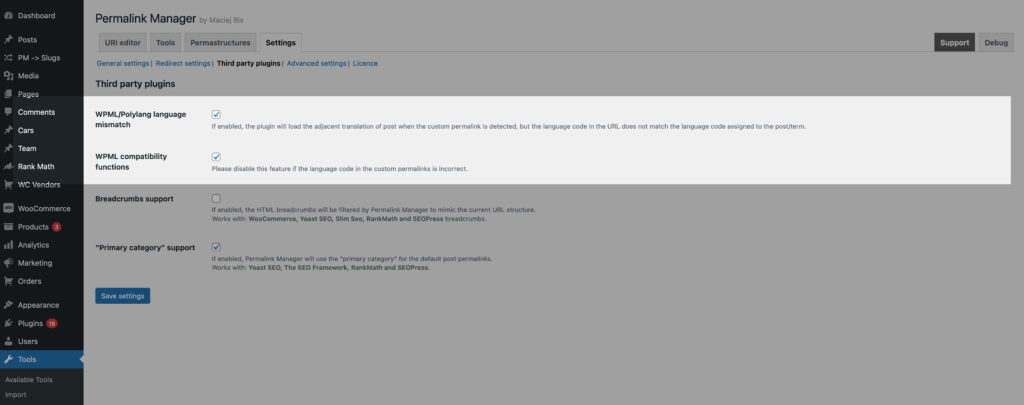
How To Fix Language URL Mismatch?
When using WPML or Polylang, in rare cases Permalink Manager can "misread" the intended language of a URL. This typically happens if you have custom rewrite rules or certain plugins active.
If translated permalinks resolve to the wrong language or fail to load correctly, try disabling the following options in Permalink Manager settings:
- WPML/Polylang language mismatch
- WPML compatibility functions
Can I Reuse the Same Slug for Different Languages?
When managing multilingual content with WPML or Polylang, you may want to keep the same URL slug across different language variants. However, WordPress prevents this by default and automatically adds numeric suffixes to duplicate slugs.
For instance, if you create a "Services" page in English and then translate it to Spanish with the same title "Services", WordPress will modify the Spanish slug:
- English:
/en/services/ - Spanish:
/es/services-2/(unwanted "-2" suffix added)
Permalink Manager allows you to use the same slug for all language versions without any numeric suffixes. The plugin detects pages based on their full URL paths and it does not depend on rewrite rules.
Language prefixes added by WPML or Polylang keep each URL unique, so the plugin can resolve the correct page every time.
Which URL Structure Is Best for A Multilingual Website?
When creating a multilingual website, URL structure is one of the factors to consider for SEO. There are three common methods for handling multilingual URLs.
- Directory-based
Format: example.com/en/page-nameIt is the most straightforward and popular option and groups translated content into subdirectories. This approach is easy to set up with most multilingual plugins and works well for SEO since all languages share the same domain authority.
- Subdomain-based
Format: en.example.com/page-nameThis structure uses subdomains for each of languages and requires DNS configuration and either wildcard or seperate SSL certificates.
- Domain-based
Format: example.com & example.frThis configuration uses separate domains for each language and is perfect for country-specific targeting and localized branding. However, it requires managing multiple TLD domains, which can be more time consuming and expensive.