Permalink Manager has the ability to dynamically alter custom permalinks, which is one of its main features. If you would like to integrate your code with the plugin, the information presented in this article may be useful to you.
This article outlines how Permalink Manager handles data storage, with a particular focus on custom permalinks and redirects. If you are interested in learning where are WordPress permalinks stored natively, check out the linked article.
Permalink Manager is designed to work seamlessly with small and medium-sized websites and WooCommerce stores. It allows you to rewrite hundreds, or even tens of thousands, of custom permalinks without complications.
Permalink Manager's Data Storage Model
How Does The Plugin Stores Its Data?
One of the key features of this plugin is its unique storage model. Instead of creating a separate entry in the database for each permalink, Permalink Manager stores all custom permalinks in a single array within the wp_options table.
This approach has a number of advantages. One of the most notable is that it reduces the number of slow SQL queries that need to be made to the database. By minimizing the number of SQL queries and leveraging PHP’s quick array operations, which run in server memory, the plugin can process the custom permalinks more efficiently.
Where Is The Data Stored?
Custom URIs, redirects, permastructures, and plugin settings are serialized and saved in the wp_options database table in order to improve the performance of the website.
This storage architecture is suitable for the majority of user scenarios, however it may not be effective if your website has thousands of posts or pages. Please see this post for further information about the plugin's performance.
Custom permalinks and redirects can be accessed as global variables to make advantage of the unique algorithm that allows Permalink Manager to detect content element when a particular URL is requested.
global $permalink_manager_uris, $permalink_manager_redirects;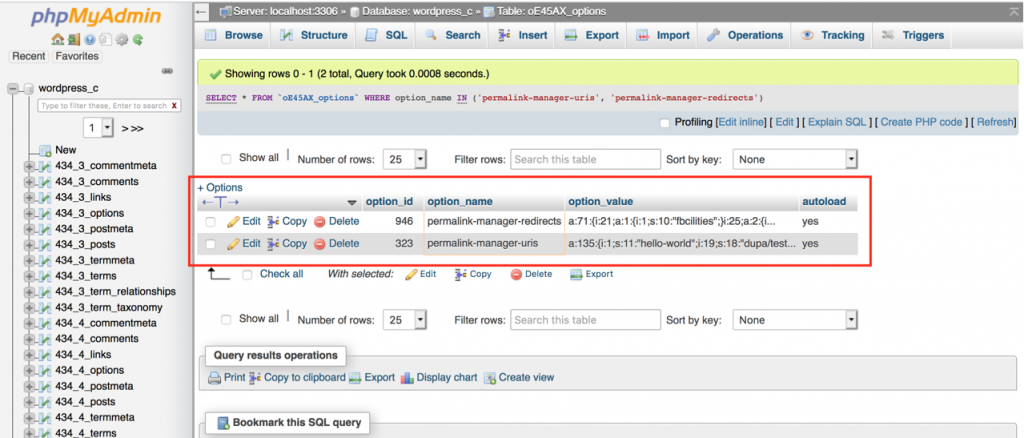
If necessary, you may preview all of the data by using the "Debug" section.
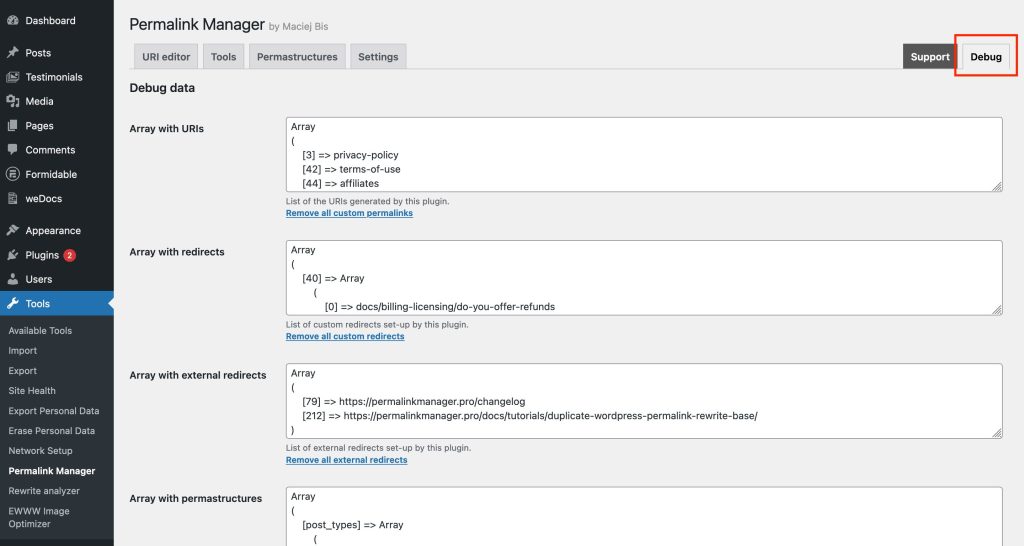
How to Filter Custom Permalinks and Redirects?
Custom permalinks
As you can see the indexes for post permalinks are integers (10, 12). The term permalinks' indexes are prefixed with “tax-” (tax-20, tax-28):
Array (
[10] => custom-uri/used-by-a-single-post
[12] => another-custom-uri/used-by-another-single-post
...
[tax-20] => custom-uri/used-by-a-single-term-tag-or-category
[tax-28] => another-custom-term-permalink-example
)One of the biggest advantages of Permalink Manager is a possibility to to dynamically manipulate the custom permalinks. You can access the permalinks array either through the global variable $permalink_manager_uris or by using the plugin's dedicated function.
function pm_filter_and_save_custom_uris() {
global $permalink_manager_uris;
########### Posts, pages, custom post type items ###########
$post_id = 12;
// A. Get the post's custom permalink using global
$post_custom_permalink = ( ! empty ( $permalink_manager_uris[$post_id] ) ) ? $permalink_manager_uris[$post_id] : '';
// B. Get the post's custom permalink using plugin's API
$post_custom_permalink_alt = Permalink_Manager_URI_Functions_Post::get_post_uri( $post_id );
########### Categories, tag, custom taxonomy terms ###########
$term_id = 34;
// A. Get the term's custom permalink using global
$term_custom_permalink = ( ! empty ( $permalink_manager_uris["tax-{$term_id}"] ) ) ? $permalink_manager_uris["tax-{$term_id}"] : '';
// B. Get the post's custom permalink using plugin's API
$term_custom_permalink_alt = Permalink_Manager_URI_Functions_Tax::get_term_uri( $term_id );
}This is a simple example. For further information on the plugin's core functions for getting, editing, and updating custom permalinks, please refer to the separate article for more details.
Custom redirects
Analogous to custom permalinks, the custom redirects array contains groups of URIs assigned to posts and term by their IDs:
Array (
[10] => Array (
[0] => first-custom-redirect/asigned-to-a-single-post
[1] => second-custom-redirect/asigned-to-a-single-post
[2] => third-custom-redirect/asigned-to-a-single-post
)
...
[tax-28] => Array (
[0] => different-first-custom-redirect/asigned-to-another-single-category
[1] => different-second-custom-redirect/asigned-to-another-single-category
[2] => different-third-custom-redirect/asigned-to-another-single-category
)
)Below you can find a very basic example that shows how the custom redirects can be edited programmatically:
function pm_filter_and_save_custom_redirects() {
global $permalink_manager_redirects;
// Set new custom redirect (Post ID: #10)
$permalink_manager_redirects[10][] = "new/custom-redirect"
// Remove one of redirects (Term ID: 28)
unset($permalink_manager_redirects["tax-28"][1]);
// Save the array in DB
update_option('permalink-manager-redirects', $permalink_manager_redirects);
}