Once you have decided on your new URL structure, the next step is to implement redirects for any existing URLs that will be changed. This will guarantee that the old URLs are automatically redirected to the new ones.
Using Permalink Manager to manage custom permalinks means your URLs will change, and this is to be expected.
To keep your SEO performance intact, it is important to set up redirects that smoothly lead visitors to the new addresses.
Without them, anyone trying to visit the old permalinks would receive a 404 error, which can result in a negative user experience.
Redirect Functions
Permalink Manager can lessen the danger of lost traffic when changing URLs by providing three different redirection functions.
The first type is dynamic and works similar to the canonical redirect included in WordPress core. The plugin dynamically determines whether the requested URL is the same as the native URL that was used prior to installation. Simply said, it will automatically redirect visitors who try to access the original URL to the new canonical URL.
The second type of redirection is used in situations in which the URL has been modified more than once. In such situations, all intermediate URL versions are kept as "extra redirects" in a database. As they are all stored in the database, you can change, remove, or add new redirect URLs.
Furthermore, you have the option to redirect any post or term to an external URL.
Canonical Redirect
WordPress can identify and handle invalid URLs to some extent. That is, when an outdated URL is requested, WordPress looks for the new, updated URL and redirects the visitor if it finds it.
Nonetheless, the aforementioned WordPress functionalities do not always operate as expected. To avoid this, the plugin offers a more solid redirect mechanism for old permalinks, which reduces the risk of organic traffic loss.
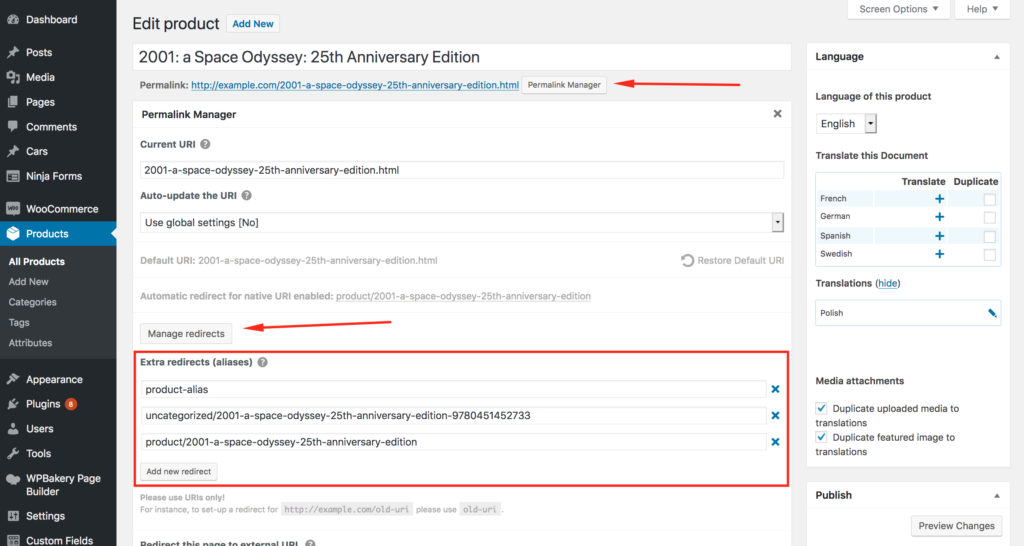
Extra Redirects (Aliases)
In addition to the canonical redirect function, the plugin allows you to create additional custom redirects for each content item. This might be particularly useful if you want to allow users to use an extra URL (alias) or redirect traffic from other, obsolete URLs.
There is one limitation here. You can only use an address as a "extra redirect" if it is not already being used as a custom permalink for another post or term. If you try to redirect to a custom permalink that is already in use for another page, the "extra redirect" will be ignored.
You may "unlock" the affected URL (alias) and allow the extra redirect by excluding the ID of the item you wish to redirect.
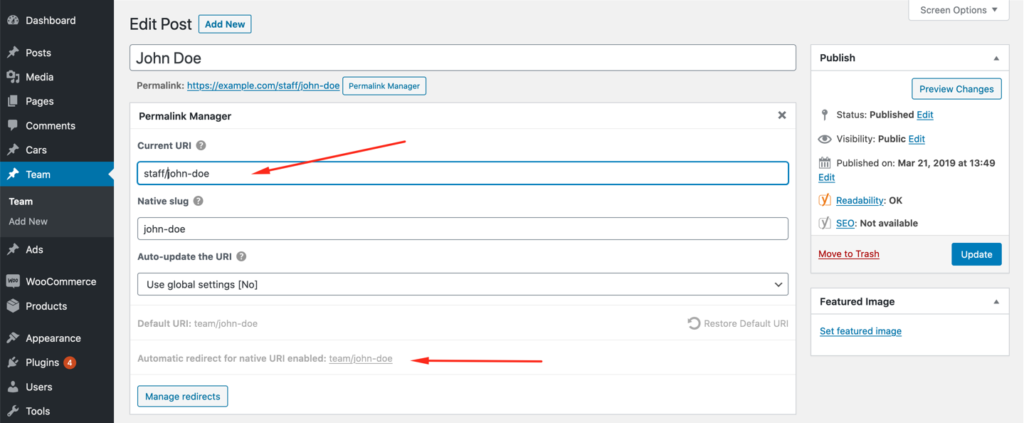
How to Manage “Extra Redirects"?
The custom redirects panel is easily accessible from the URI Editor. To open it, click the "Permalink Manager" button located under the title field. Then, at the bottom, click the "Manager Redirects" button.
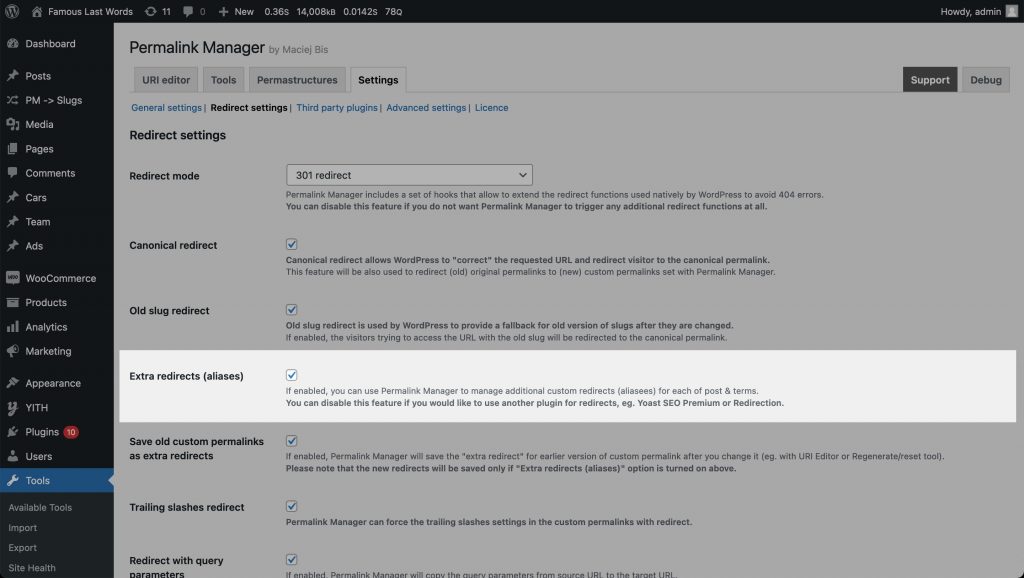
How to Enable This Feature?
The extra redirects functionality is enabled by default in the plugin settings. However, if you need to, you can easily turn it off. This may be the case, for instance, if you handle redirects with another plugin, such Yoast SEO Premium or Redirection.
To do this, open the plugin settings page and deselect the "Extra redirects (aliases)" checkbox.
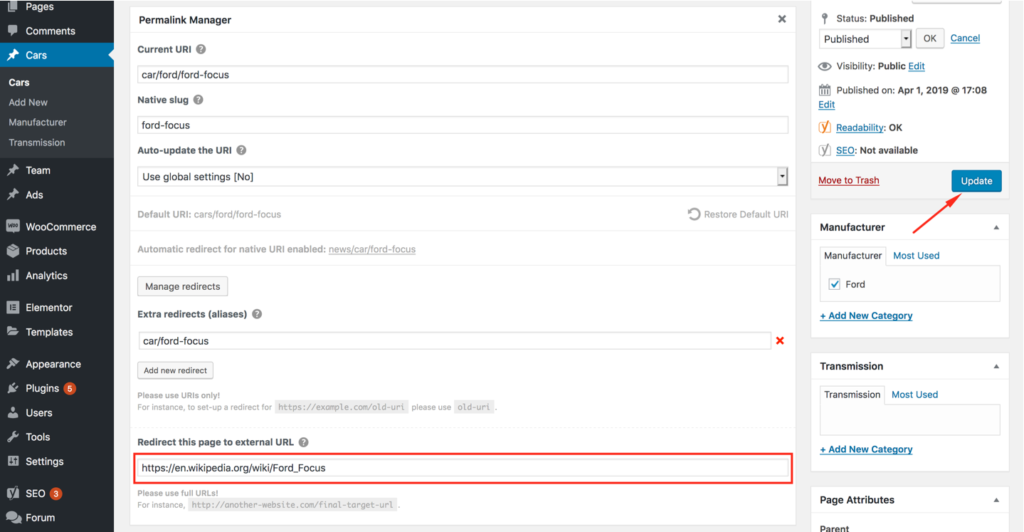
Redirect to External URL
You may also use Permalink Manager Pro to redirect any term, page, or post to an external URL. Unlike internal redirects, you must type the whole URL address into the input field:
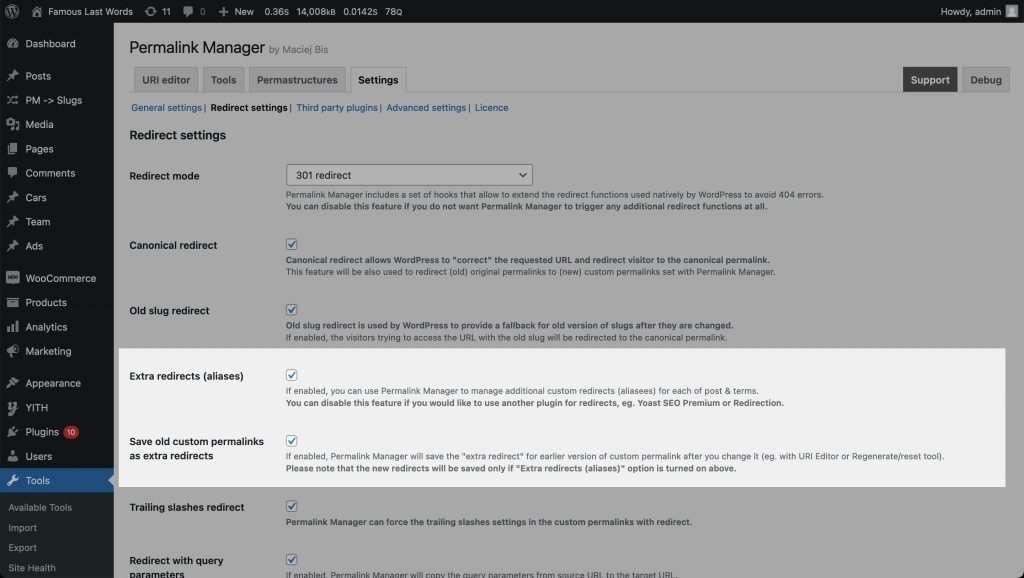
How to "Save Old Custom Permalinks As Extra Redirects"?
Extra redirects can also be generated for previous versions of custom permalinks. This is not rare, and it might be really handy if you decide to change the URLs multiple times.
If you decide to change the custom permalinks on your website at some point, the "Save old custom permalinks as extra redirects" feature in Permalink Manager Pro can be extremely useful. This feature allows you to automatically define a redirect for the old version of a URL whenever you change it again.
To enable this, go to the "Settings -> Redirect settings" section in Permalink Manager Pro settings. Then select the "Extra redirects (aliases)" and "Save old custom permalinks as extra redirects" options. This will save the previous version of the URL as a redirect for the new address.
As long as "Save old custom permalinks as extra redirects" option is turned on, all the previously used permalinks will be automatically saved as redirects. This would be case, if you either adjust both individual permalink or change the general permalink format (with "Permastructures" & "Regenerate/reset" tool).
Troubleshooting
Managing a WordPress website often involves using a variety of plugins, and sometimes these can interfere with each other in unexpected ways. This can lead to unexpected redirect issues, such as redirect loops.
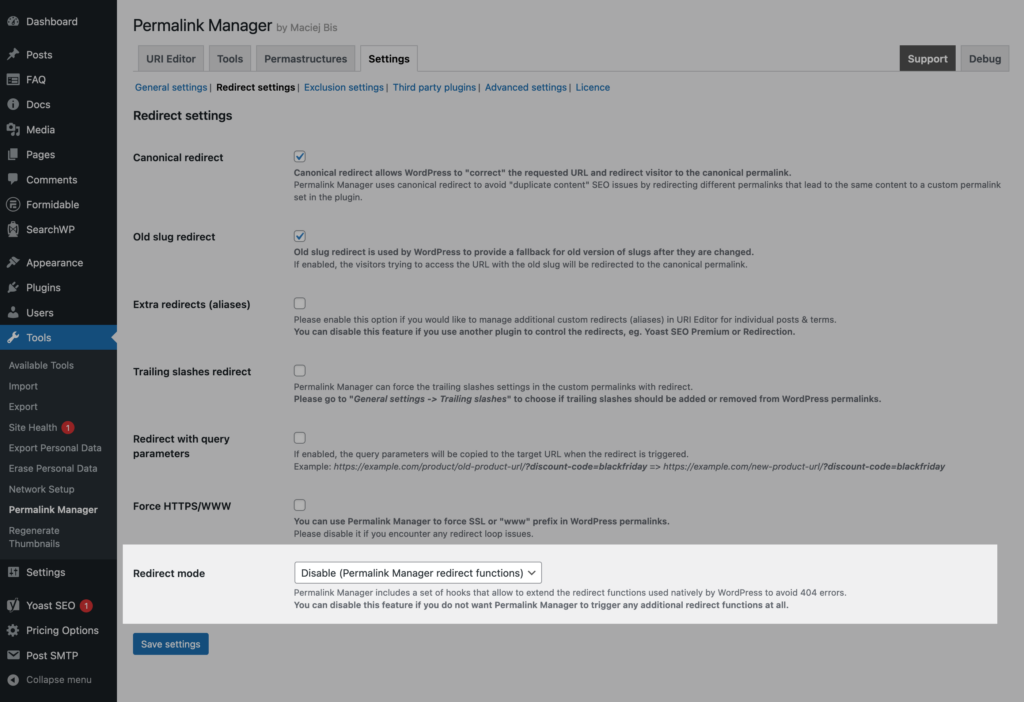
How to Disable All Redirect Functions?
If you are already using other redirect plugins, there is no need to duplicate this functionality. In this case, you can disable all redirect functions provided in the plugin in its settings.
How To Disable The Redirects Conditionally?
In some scenarios, automatic redirects managed by Permalink Manager are conflicting with other plugins or custom code.
If you do not want to disable the redirects completely, you can conditionally stop them by using a custom code snippet. This way, you can control redirects based on specific criteria, such as post/category ID, or query parameters:
/**
* Conditionally stop Permalink Manager redirect functions
*
* @param string|false $target_url The redirect target URL
* @param string $redirect_type The type of redirect being processed (e.g., 'native_redirect', 'old_slug_redirect').
* @param WP_Post|WP_Term|null $queried_object The currently queried object (post, term, or null).
*
* @return string|false Modified URL or false to stop the redirect.
*/
function pm_conditional_stop_redirect( $target_url, $redirect_type, $queried_object ) {
global $wp_query;
// A. Stop the redirect on a specific page or post (replace 123 with your specific post ID).
if ( ! empty( $queried_object->ID ) && $queried_object->ID == 123 ) {
$target_url = false;
}
// B. Stop the redirect on a specific category or term (replace 456 with your specific term ID).
if ( ! empty( $queried_object->term_id ) && $queried_object->term_id == 456 ) {
$target_url = false;
}
// C. Stop the redirect if a specific query argument is present in the query object.
if ( ! empty( $wp_query->query_vars['some_query_argument'] ) ) {
$target_url = false;
}
return $target_url;
}
add_filter( 'permalink_manager_filter_redirect', 'pm_conditional_stop_redirect', 5, 3 );